
Lower Back & Pelvis
Lower back pain is very common and affects many people at some point in their lives.
Our physiotherapists at Platinum Physiotherapy provide specialist assessment and treatment for people with lower back problems and use a variety of treatment techniques to help this condition.
There are many structures around the pelvis including your joints and soft tissue. A skilled assessment of your back and pelvis will allow your physiotherapist to understand the nature of your problem and develop a treatment plan to help you. Lower back and pelvic problems we commonly treat include:
- Acute Low Back Pain
- Back Strain
- Disc Prolapse
- Facet Joint Pain
- Low Back Pain
- Lumbago
- Scoliosis
- Slip Disc
- Spondylolisthesis
- Spondylolysis
- Coccydynia
- Gluteal strain
- Hamstring origin tendonitis
- Ischiogluteal bursitis
- Piriformis syndrome
- Referred pain
- Sacroiliac joint pain
An initial assessment will see how your current problem is affecting your everyday activities. Individualised treatment goals will then be formulated between you and your physiotherapist with reference to the findings during the assessment. Your physiotherapist will also advise you on exercise, pacing, reduction in aggravating factors and pain medication to reduce any anxiety and make sure you get the most out of your treatment.
Many people with lower back problems benefit from physiotherapy and go on to make significant long term improvements. Physiotherapy treatment will help you manage your pain, improve your strength and flexibility and facilitate your recovery.
Acute Low Back Pain
What is acute low back pain?
Acute low back pain is usually of sudden onset and is often triggered by a relatively minor movement such as bending to pick up an object. Acute or short-term low back pain generally lasts from a few days to a few weeks. People with chronic low back pain may also have acute episodes that may become more frequent and require less initiation over time.
What causes acute low back pain?
Most acute back pain is mechanical in nature which means it is caused by trauma to the lower back or a disorder such as arthritis. Pain from trauma may be caused by a sports injury, work around the house or in the garden, or a sudden jolt such as a car accident that place stress on spinal bones and tissues.
What are the effects/symptoms of acute low back pain?
A person with initially experience sharp pain which may develop over a period of hours due to the development of inflammation.
The pain is usually in the lower lumbar area and may be central, to both sides, or to one side. It may radiate to the buttocks, hamstrings or lower leg. Sharp, stabbing pain in a narrow band down the leg is radicular pain and is associated with nerve root irritation, sometimes as a result of a ‘slipped disc’. More commonly, the pain the patient feels in the buttock and hamstring is referred from the lumbar spine.
Physiotherapy for acute low back pain
A person with acute low back pain will benefit from physiotherapy treatment.
Our physiotherapists at Platinum Physiotherapy provide specialised physiotherapy treatment to reduce pain and inflammation and return you to your everyday activities with confidence and success.
Your physiotherapist will provide you with individual advice regarding the best management of your acute lower back pain. Physiotherapy treatment may include:
- Ice therapy
- Joint mobilisation or manipulation
- Soft tissue massage to relieve pain, stiffness and muscle spasm
- Postural management
- Ergonomic assessment
Individualised back exercise program. As your symptoms resolve, your physiotherapist can teach you progressive stretching, strengthening and core stability exercises to minimise the risk of a reoccurrence.
It is important to commence physiotherapy treatment as soon as possible after your injury for the best possible results.
Contact Us
Back Strain
What is a back strain?
A back strain or ‘pulled’ muscle in the lower back is a frequent source of back pain characterised by stretching of tearing of a muscle.
What causes a back strain?
A back strain can be caused by strenuous activity like lifting a heavy object in an incorrect manner by bending the back rather than the knees, sharp sudden twisting movements, or even due to standing for long periods of time.
The spine is held upright by muscles and ligaments and the over-stretching or tearing of these muscles can occur if the muscle suddenly contracts or is stretched too far. When a back strain or sprain occurs, there is inflammation of the soft tissue that causes pain and possibly back spasms. Back strains and sprains can also be caused by poor posture, poor muscle tone in the back and abdomen, emotional stress or excessive weight or pregnancy.
What are the symptoms/effects of a back strain?
People with a back strain frequently feel pain that can appear either side of the back or in the upper buttocks and can get worse with muscle spasms as they occur.
Physiotherapy for a back strain
It is important to consult a physiotherapist following your injury hasten your recovery and for the best possible outcome.
At Platinum Physiotherapy, we provide individualised physiotherapy treatment which will facilitate healing, reduce pain and stiffness and get you back to work and your hobbies sooner.
Your physiotherapist will initially assess your current symptoms, range of movement, muscle strength and function in order to develop a progressive rehabilitation program.
Physiotherapy treatment for a muscle strain may include:
- Advice on how to modify your activity to support and protect the muscles and prevent any further damage
- Gentle active range of movement exercises to loosen up muscles and reduce pain
- Ice therapy to minimise inflammation and swelling
- Ultrasound to promote healing
- Heat therapy and soft tissue massage to increase circulation and relax muscle spasms
- Progressive and individualised exercise program, for the abdominal or ‘core’ muscles and back muscles to increase strength and stability of the spine.
- Your physiotherapist will develop a progressive rehabilitation program to ensure you return to activities safely and effectively
Physiotherapy treatment will hasten the recovery process and get you back to the daily and sporting activities you enjoy as quickly as possible.
Contact Us
Disc Prolapse
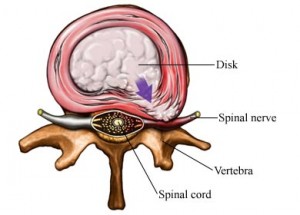 What is a disc prolapse?
What is a disc prolapse?
A disk prolapse, or ‘slipped disk’, occurs when the thick paste-like disc nucleus is pushed out through a tiny defect in the fibrous disc wall. This bulge of nucleus can irritate the nerve root causing pain, which may radiate down the leg.
What causes a disc prolapse?
A disc prolapse usually occurs when pressure is placed on the spine when lifting a heavy object in the wrong way. A direct injury such as a fall or a whiplash accident can cause a disc prolapse.
What are the symptoms/effects of a disc prolapse?
People with a disc prolapse typically present with acute low back pain and/or leg pain following a relatively trivial movement usually involving bending forward. Pain is often aggravated by sitting, bending, lifting, coughing and sneezing. Pain is usually eased by lying down, particularly on the non-painful side, and is often less in the morning after a nights rest.
Physiotherapy treatment for a disc prolapse
Physiotherapy treatment is very effective at reducing pain and stiffness and improving muscles strength and flexible following a disc prolapse.
Your physiotherapist at Platinum Physiotherapy will develop an individually tailored exercise plan for you to relieve pain, keep you strong and flexible and help prevent any further damage being caused to your back.
Physiotherapy treatment in the acute phase will consist of advice on how to modify activity, and use of painkillers. As the acute episode settles, treatment for disc prolapse may include:
- Extension exercises to relieve nerve root irritation and pain
- Heat therapy
- Soft tissue massage
- Back exercise program including strengthening and stretching exercises to restore normal pain-free movement to the area and stabilise the spine.
- Joint mobilisation to relieve pain and stiffness
- Acupuncture
- Electrical stimulation such as TENS to help with pain
- Postural advice
Your physiotherapist will support your through your exercise program to ensure you are maintaining a correct posture and strengthen the core stabilising muscles and back muscles safely and effectively, so that you can return to work and sporting activities as soon as possible.
Contact Us
Facet Joint Pain
What is Facet Joint Syndrome?
Facet Joint syndrome is pain arising directly from the facet joints. The facet joints are at either side of the intervertebral joints in your back. Their role is to prevent excessive movement, and provide stability for the spine. When the facet joints are functioning correctly they move freely to control the movement of the spine.
What causes Facet Joint Syndrome?
A fall and blow to the body sustained playing sport or as a result of a car-crash, for example, can put excessive pressure on the facet joints bringing about acute pain. Extending the spine or bending towards the affected side will exacerbate the pain in the facet joint.
Pain in the facet joints can also be caused by sudden excessive movements that can have a great impact on the joint itself, or degeneration within the joint, resulting in the pain lasting longer than a few days. In the event of some kind of trauma there in an inflammatory reaction causing swelling in these joints which is a component factor in the joint pain. Pain can also be caused due to an impingement on a nerve within the joint.
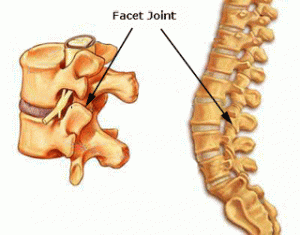 What are the Symptoms of Facet Joint Syndrome?
What are the Symptoms of Facet Joint Syndrome?
The main symptom of facet joint syndrome is pain just to one side of the spine and the spine will generally feel very stiff in the mornings. Often the muscles in the area of pain go into spasm.
Physiotherapy for Facet Joint Syndrome
At Platinum Physiotherapy, we provide specialised assessment and treatment for people with facet joint pain. Physiotherapy treatment will reduce pain and stiffness by concentrating on improving range of movement and strength in the back.
Physiotherapy treatment for facet joint pain may include:
- Soft tissue massage
- Stretching exercises for the back and hip joints
- Joint mobilisation or manipulative treatment
- Structured exercise program to strengthen the back muscles and help to stabilise the spine.
- Advice on how to modify activity
- Activities to improve posture
Physiotherapy will facilitate healing, promote recovery and get you moving better so that you can return to work, hobbies, and everyday tasks as soon as possible.
Contact Us
Low Back Pain
What is Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain can be either an acute (sudden and short term) or chronic (long-term and often getting progressively worse) disabling condition that affects many people at some stage in their life. Lower back pain can also be described as a symptom of many other conditions.
What causes Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain can be caused by a variety of factors and is usually categorised as mechanical, inflammatory, metabolic, referred pain from elsewhere, or can even be caused by depression.
Lower back pain can be caused by an injury or a form of trauma, like a sports injury, a car accident or a fall which damage the muscles, discs or joints in the lower back.
Poor posture can be another and poor body mechanics such as lifting without bending the knees.
Other causes can be particular conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and degeneration of the discs between the vertebrae.
What are the symptoms/effects of Lower Back Pain?
Pain in the lumbosacral area (lower part of the back) is the primary symptom of low back pain which may be worse at night or after sitting for long periods. This pain may radiate down the front, side, or back of your leg, or it may be confined to the low back. Your may also experience numbness, pins and needles or weakness if your injury is irritating a nerve root.
Physiotherapy for Lower Back Pain
Physiotherapy treatment is beneficial for people with lower back pain. Physiotherapy uses a combination of hands-on techniques, advice and exercise to promote recovery and return you to your normal level of function as quickly as possible.
Your rehabilitation program may include:
- Postural advice and adaptations
- Exercise programmes including aerobic exercise, muscle strengthening and stretching
- Joint mobilisations and manipulations
- Trigger point therapy
- Massage
- Ultrasound
Your physiotherapist at Platinum Physiotherapy will advise and support you through an individualised treatment program tailored to your lifestyle and hobbies to reduce pain, stiffness and improve strength and flexibility.
Contact Us
Lumbago
What is lumbago?
Lumbago is a term describing general mid to lower back pain.
What causes lumbago?
The exact causes of lumbago are unknown or rather its cause could be put down to a variety of things such as lifting objects that are too heavy and not lifting them in a proper way, overuse of the back, or as a result of some other condition you may be suffering from.
A common cause of back ache is weak stomach muscles, which increases the stress on the back muscles.
Several factors can contribute to back pain, like a sprain or spasm in a muscle or ligament, compression of the spine, or bulging or ruptured discs, all of which can put pressure on the nerves in the area. Back pain can also result from more serious disorders ranging from a trapped nerve to diabetes and cancer, and although it is often very difficult to determine the exact cause of back pain, some people may develop it for no apparent reason.
What are the symptoms of Lumbago?
- Symptoms of lumbago include:
- Pain in the lower back that doesn’t radiate down through the legs
- Stiffness of the back especially in the morning
- Poor posture or an “S” shape in the spine.
- Lumbago may be accompanied by other symptoms such as:
- Loss of sensation in the soles of the feet or in the calf region
- Loss of plantar flexion (pointing) of the foot
- Back stiffness in other areas of the spine
Physiotherapy for lumbago
A person with lumbago will benefit from physiotherapy treatment.
Treatment will reduce your pain and stiffness, increase muscle strength to help support your back and improve your posture to help return you to return to everyday and sporting activities as quickly and safely as possible.
Physiotherapy treatment for lumbago may include:
- Advice on your posture and exercises to improve it
- Advice on what you should be avoiding
- Heat therapy
- Ultrasound
- Massage
- Strengthening program, weak stomach muscles are often a cause. Regular gentle stomach muscle exercise in conjunction with back exercises may make a big difference
- Stretching exercises to relieve stiffness and pain
- Joint manipulation/mobilisation techniques
Your rehabilitation program will be tailored to you to ensure you get the most out of your treatment and continue to make improvements in the long term.
Contact Us
Scoliosis
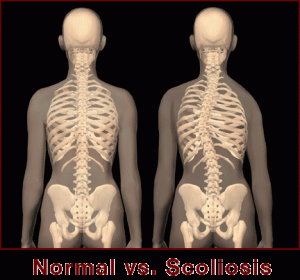 What is scoliosis?
What is scoliosis?
Scoliosis is the most common deformity of the spine comprising two abnormalities of the spine; a lateral curvature meaning the spine bends from side to side creating an ‘S’ shape; and a rotation of the spine, which causes a twisting effect of the vertebral bodies. This deformity of the spine can often cause pain and fatigue but this depends on the degree of the curve.
What causes Scoliosis?
The cause of Scoliosis can point to various factors such as genetic, neuromuscular, hormonal or growth factors, though the cause is usually multi-factorial. In fact, the most common form of scoliosis is called “idiopathic scoliosis” which means that the cause is unknown, and furthermore it can affect people of different ages.
The most common type of scoliosis is idiopathic adolescent scoliosis. There are cases however of congenital scoliosis that is an abnormality in the development of the vertebrae, and it is this failure of the spine to develop normally that causes scoliosis and sometimes deformity.
Scoliosis can also be non-structural which means that a problem in another part of the body, like a discrepancy in leg length, can cause a curve in the spine or an imbalance in the muscles caused by one sided activities such as racket sports or something simpler like a child carrying a heavy bag on one shoulder all day at school.
What are the Symptoms of Scoliosis?
The symptoms of scoliosis include:
- Asymmetric alignment in the body such as uneven hip and shoulder levels
- One prominent shoulder blade
- Dissimilar size or location of breasts in females
- Often there is a muscle masses that causes a “hump” on one side of the body.
- Pain
- Fatigue
The pain caused by the irregular shaping of the spine and the resulting muscular compensation can vary from being mild to acute, and often affects the area directly surrounding the spine itself. Often there is stiffness in the back and neck.
Physiotherapy treatment for Scoliosis
Physiotherapy will help to minimise the impact of the scoliosis on your day to day life
Physiotherapy treatment can help to strengthen the supporting muscles of the spine and correct poor posture.
Your physiotherapist at Platinum Physiotherapy will develop a structured rehabilitation program which may include:
- Continual postural management including advice and adaptations. Mirror therapy is often used to increase awareness poor posture and correct it accordingly.
- Stretching and strengthening exercises for the back and shoulders
- Manipulation and mobilisations
- Ultrasound
- Soft tissue massage
- Ergonomic assessment
- In more serious forms of Scoliosis, bracing (especially in children) or surgery may be needed. Your physiotherapist will advise if this option is required
Physiotherapy treatment will reduce pain and stiffness, increase muscle strength and improve your posture so you can continue with you everyday and sporting tasks to your maximum ability.
Contact Us
Slipped Disc
The spine is made up of the vertebrae that have cartilage discs between them. The discs consist of a circle of connective tissue with a central gel-like core. This makes the spine flexible and at the same time acts as a protective buffer.
In the centre of this column of vertebrae and discs is the spinal canal, which contains the spinal cord stretching from the brain stem down to the first or second lumbar vertebra. It continues as a bundle of nerve fibers. Between each vertebra, the spinal cord has nerve root connections to other parts of the body.
The spine is connected to the ribs at the chest and is divided into three parts:
- Neck (cervical vertebrae)
- Chest (thoracic vertebrae)
- The lower back (lumbar vertebrae)
What is a slipped disc?
A slipped disc is the name given to prolapsed intervertebral discs that put pressure on the spinal cord and nerve root causing pain. The term is in fact misleading because an intervertebral disk is unable to slip or slide. Slipped discs most commonly occur in the lumbar spine, at the bottom of the back, between the fourth and fifth vertebra (L4/ L5).
What causes a slipped disk?
Repeated overuse of certain tasks, during bending, lifting, and sporting activities can cause a slipped disk. Usually there is one offending movement that will be the catalyst for a prolapse to occur. Overuse of certain spinal disks in the back can lead to degeneration of the outer layer of the intervertebral disc and, if this degeneration is sufficient, the gel-like nucleus material is liable to prolapse out of the disc. If the prolapse is pressing on the nerve root this will cause you pain. Other causes include stress fractures and also genetics may also play a part in the probability of a slipped disk occurring.
What are the Symptoms of a slipped disk?
Onset of sudden and severe pain in the back made worse by flexed positions such as sitting. Often the prolapse direction means that pressure is put on the sciatic nerve which produces pain in the buttock, hamstrings, the back of the knees, the calf or the heel.
Sometimes symptoms may include numbness and loss of motor control over the leg.
Contact Us
Spondylolisthesis
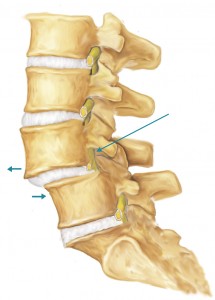 What is Spondylolisthesis?
What is Spondylolisthesis?
Spondylolistheisis is the slipping of one vertebra forward relative to another. It is often associated with defects that usually develop in early childhood and has a definite family predisposition. Stress fractures that develop due to athletic activity rarely result in spondylolisthesis. Spondylolisthesis is most commonly seen in children between the ages of 9 and 14. In the majority of cases it is the L5 vertebra that slips forward relative to S1.
What causes Spondylolisthesis
Causes of spondylolisthesis include:
- Spondylosis
- Genetics
- Weakened facet joint which can occur in children
- Infections and degeneration
- Repetitive hyperextension of the spine that comes with such sports as gymnastics, diving, weightlifting and football
Classification of Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is classified according to the degree of slip of the vertebra. A grade I slip denotes that a vertebra has slipped up to 25% over the body of the vertebra underlying it; in a grade II slip the displacement is 25%; in a grade III slip, 50%; and in a grade IV slip; greater than 75%.
Grade I spondylolisthesis is often symptomatic and the patients may be unaware of the defect. Patients with grade II or higher slips may complain of low back pain, with or without leg pain. The back pain is aggravated by extension activities.
What are the symptoms/effects of spondylolisthesis
The most common symptom of spondylolisthesis is lower back pain. This is often aggravated by exercise especially with extension of the lumbar spine. Other symptoms include stiffness and pain, numbness, tingling or weakness in the legs due to nerve root irritation.
Diagnosis of spondylolisthesis
A physiotherapist or doctor will perform a physical examination to identify the nature of your back pain. You will be referred for an X-ray too see if a vertebra is out of place, and confirm a diagnosis of spondylolisthesis.
Physiotherapy treatment
At Platinum Physiotherapy, we provide specialised assessment and treatment for children and adults with spondylolisthesis.
Physiotherapy treatment of people with grade I or grade II symptomatic spondylolisthesis involves rest from aggravating activities, advice about correct posture and lifting techniques while you are recovering combined with abdominal and extensor stabilizing exercises and hamstring stretching.
An exercise program will also be developed and tailored to your symptoms and current level of activity to ensure you keep your back strong and flexible but don’t do any more damage.
If there is stiffness of the joints above or below the slip on clinical assessment, these joints will be mobilised using hands on techniques.
Physiotherapy treatment will be focused on reducing pain, improving posture, increasing strength of the muscles to help stabilise your back and getting you back to your everyday activities and hobbies with confidence and success as soon as possible.
Contact Us
Spondylolysis
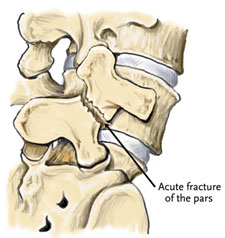 What is Spondylolysis?
What is Spondylolysis?
Spondylolysis is a stress fracture of the pars interarticulari, a bone that connects the upper and lower segments of the facet joints in your spine allowing movement. It often occurs in young athletes involved in sports that require hyperextension and rotation.
What is the cause of Spondylolysis?
Spondylolysis is caused by weakness of the pars interarticularis. The exact cause of the weakness of the pars interarticularis is unknown. One cause may be overuse and that repetitive trauma to the lower back can weaken the pars interarticularis. This commonly occurs in sports requiring repetitive movement such as gymnastics, weight lifting, athletics, and football. Another cause points to genetics (heredity) as a factor, suggesting that some people are born with thin vertebrae, which places them at higher risk of spondylolysis.
The fracture usually occurs on the side opposite to the one performing the activity i.e. left-sided fractures in right-handed tennis players.
What are the symptoms/effects of Spondylolysis?
The patient will complain of unilateral low back ache occasionally associated with buttock pain. The pain is aggravates by movements involving extension.
Diagnosis of Spondylolysis
Diagnosis of Spondylolysis can be made by a physiotherapist or doctor after conducting a thorough subjective history and physical examination. An X-ray be required to help to confirm a diagnosis.
Physiotherapy treatment for Spondylolysis
At Platinum Physiotherapy we provide comprehensive assessment and treatment for people with spondylolysis.
Early diagnosis and rehabilitation is essential in this type of injury for the best possible recovery.
Physiotherapy treatment will be tailored to you current symptoms and lifestyle but may include:
- Restricting athletic activity responsible for the pain
- Cold or heat therapy to promote healing and reduce muscle spasm
- Stretching exercises for the hamstring and gluteal muscles
- Gentle active range of movement exercises to relieve stiffness and keep your back moving normally while you are still healing
- Strengthening the abdominal and back extensor muscles once pain free range of movement has been achieved.
- Sport specific exercises
Your rehabilitation program will be structured so that you progress safely and effectively and eventually return to the activities you enjoy to the best of your ability.
Contact Us
Coccydynia
 What is coccydynia?
What is coccydynia?
Coccydynia is pain in the area of the coccyx or tailbone and can be anything from discomfort to acute pain, which is aggravated by sitting down.
What causes coccydynia?
Coccydynia occurs when your coccyx, or the surrounding tissue, becomes damaged and can be caused by many different factors.
The various possible causes of coccydynia include:
- Childbirth. This can cause the muscles and ligaments to overstretch around your coccyx compromising the stability of the coccyx bone.
- Direct injury. This can occur when you fall on the base of your spine when skiing, gymnastics or horse riding.
- Repetitive strain injury. Repetitive movement such as leaning forward and stretching the base of your spine in sports such as cycling or rowing can cause coccydynia.
- Poor posture. Sitting in an awkward position for a long period of time, such as at work or while driving, can put too much pressure on your coccyx
What are the symptoms/effects of coccydynia?
The main symptom of coccydynia is pain and discomfort at the base of your spine, where the coccyx is located which is usually made worse when you are sitting. The severity of the pain varies from person to person, and it can get worse as time passes. Coccydynia can have a significant impact on everyday activities such as sitting, driving and bending over.
Diagnosis of coccydynia
A physiotherapist or a doctor will take a detailed history and conduct a thorough physical examination to confirm a diagnosis.
Physiotherapy for coccydynia
Physiotherapy treatment will help to reduce your pain and get you back to your everyday tasks with ease and confidence as soon as possible.
Your physiotherapist at Platinum Physiotherapy will ease painful symptoms by stretching and manipulating the muscles around your coccyx. This will help to relieve pain and discomfort, particularly if your coccyx has been displaced from its normal position.
Other treatment techniques used for coccydynia include:
- Heat therapy to reduce pain and stiffness
- Soft tissue massage to promote healing
- Posture advice and exercises to correct it
- Exercises to strengthen and muscles around the base of your spine once pain has settled
- Sport specific exercises
Your physiotherapist will develop a graduated rehabilitation program tailored to you, which will facilitate healing and return to everyday and sporting activities in a safe an effective way.
Contact Us
Gluteal strain
What is a gluteal strain?
A gluteal strain is when one of the muscles in your buttocks is stretched or torn causing pain and stiffness.
What causes a gluteal strain?
A gluteal strain is commonly caused by running or jumping in sports such as hurdling or dancing.
What are the symptoms/effects of a gluteal strain?
The main symptom of a gluteal strain is pain. You may experience pain when walking up or down stairs, sitting and when moving backwards. Other symptoms may include:
- Stiffness in the gluteal muscles
- Weakness of the gluteal muscles
- Bruising on the buttocks (if blood vessels are broken)
Physiotherapy for a gluteal strain
At Platinum Physiotherapy we provide individualised assessment and treatment for people with gluteal strains.
The goal of physiotherapy is to return you to your sport and everyday activities as soon as is safely possible. If you return too soon you may worsen your injury, which could cause more damage.
Your physiotherapist will support you through a progressive treatment program tailored to you which may include:
- Advice on how to change your sporting activity while your injury is still healing
- Ice/Heat therapy to promote healing and reduce pain
- Ultrasound to accelerate healing
- Soft tissue massage to reduce muscle tightness
- Stretching exercises to increase joint range
- Buttock hip and leg strengthening exercises
- Sport specific exercises
- Gradual return to activity
Return to you sport or activity will be determined by how soon the injury area recovers not by how many days or weeks it has been since your injury occurred.
It is important to commence physiotherapy treatment as soon as possible to hasten your recovery and get you back to your activities sooner.
Contact Us
Hamstring origin tendonitis
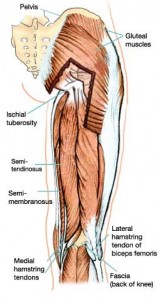 What is hamstring origin tendonitis?
What is hamstring origin tendonitis?
Hamstring origin tendonitis is a condition characterised by inflammation and damage to the hamstring tendon where is attaches to the pelvis, causing pain in the buttock.
What causes hamstring origin tendonitis
Hamstring origin tendonitis most commonly occurs due to repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on the hamstring tendon, such as running, jumping or kicking activities. Hamstring origin tendonitis may also occur suddenly due to a high force going through the hamstring tendon beyond what it can withstand, such as rapid acceleration in sprinting and football.
What are the symptoms/effects of hamstring origin tendonitis
The most common symptom of hamstring origin tendonitis is pain in the lower buttock. People may also experience an ache or stiffness in the buttock that is made worse by activity such as running, jumping or kicking.
Physiotherapy treatment for hamstring tendonitis
A person with hamstring tendonitis will benefit from physiotherapy treatment.
Physiotherapy will initially assess your current symptoms, range of movement and muscle strength in order to develop an appropriate treatment programme for you and your lifestyle.
Physiotherapy treatment for hamstring tendonitis may include:
- Soft tissue massage
- Electrotherapy (e.g. ultrasound)
- Individualised stretching program
- Ice or heat treatment
- Exercises to improve strength, flexibility and core stability.
- A gradual return to activity program specific to your sports. This may include a running program comprising of progressive acceleration and deceleration running drills.
Your physiotherapist at Platinum Physiotherapy will advise you on which exercises are most appropriate you and when they should be commenced and how to prevent re-injury
Physiotherapy treatment is vital to hasten the healing process, promote recovery and ensure you get back to you sporting activities in the most effective way.
Contact Us
Ischiogluteal bursitis
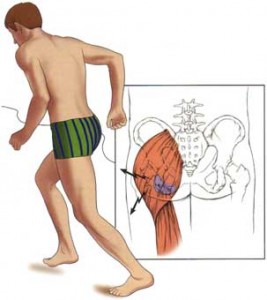 What is Ischiogluteal bursitis?
What is Ischiogluteal bursitis?
Ischiogluteal bursitis is inflammation to the ischiogluteal bursa at the base of the pelvis, causing pain and reduced activity. The ischiogluteal bursa is a small sac filled with lubricating fluid to reduce friction between adjacent soft tissue layer and lies between the hamstring tendon and the pelvis.
What causes Ischiogluteal bursitis?
Ischiogluteal bursitis is commonly caused by repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on the ischiogluteal bursa such as prolonged sitting or repetitive running, jumping or kicking activities. Ischiogluteal bursitis can also be caused by direct trauma such as a fall on a hard surface.
What are the symptoms/effects of Ischiogluteal bursitis?
The main symptom of ischiogluteal bursitis is pain in the lower buttock. This pain is often aggravated by sitting for long periods walking, running, jumping, kicking or climbing stairs.
Diagnosis of Ischiogluteal bursitis
Diagnosis of ischiogluteal bursitis can be made by a physiotherapist or doctor following a thorough subjective and objective examination.
Physiotherapy for Ischiogluteal bursitis
Physiotherapy treatment should commence as soon as possible for a speedy recovery and return to sporting and everyday activities.
Physiotherapy will reduce pain and increase muscle strength and flexibility of the surrounding muscles to ensure an optimal outcome.
Your rehabilitation program will be tailored to you but may involve:
- Soft tissue massage of the muscles in the surrounding area to reduce pain and stiffness
- Ultrasound to promote healing
- Muscle stretching to release tension
- Joint mobilisation
- Ice or heat treatment
- Progressive exercises for the hip, buttocks and legs to improve strength and flexibility
- Advice about how to modify activity
- Sport specific exercises emphasising a gradual return to activity
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy will significantly decrease your recovery time and prevent the likelihood of it happening again.
Your physiotherapist will support you through a progressive treatment program and advise you which exercises are most appropriate for you for the best possible recovery and success in the long term.
Contact Us
Piriformis Syndrome
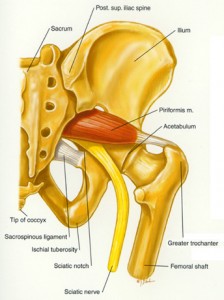 The piriformis muscle is a tiny muscle running from the base of your spine to the top of the thighbone that is deep inside the buttock and rotates the leg outwards. The sciatic nerve runs very close to this muscle and in some cases may even run through it.
The piriformis muscle is a tiny muscle running from the base of your spine to the top of the thighbone that is deep inside the buttock and rotates the leg outwards. The sciatic nerve runs very close to this muscle and in some cases may even run through it.
What is Piriformis Syndrome?
Piriformis syndrome is when the piriformis muscle becomes tight and therefore inadvertently puts pressure on the sciatic nerve. The disorder therefore causes pain and tingling and numbness in the buttocks in the area in which the sciatic nerve exists.
What causes Piriformis Syndrome?
Piriformis Syndrome is most commonly caused by other muscles being tight or not working sufficiently and therefore putting more strain on the piriformis.
Muscle imbalances (meaning one muscle being more powerful than the other causing a tug of war effect) pull the hip joints and pelvis out of place and this changes this position alteration often tightens the piriformis muscle which in turn places pressure on the nerve.
What are the Symptoms of Piriformis Syndrome?
Symptoms of piriformis syndrome include pain in the buttocks that may radiate down the leg. It can often be mistaken for sciatica.
Physiotherapy Treatment for Piriformis Syndrome
People with piriformis syndrome do well with appropriate physiotherapy. This often involves massage and stretches to the piriformis muscle.
A graduated flexibility and strengthening program guided one of our physiotherapists at Platinum Physiotherapy will accelerate healing and recondition the piriformis muscle. This is essential to reduce the likelihood of injury recurrence.
Your rehabilitation program will focus on restoring normal activity by:
- Heat and cold therapy
- Ultrasound to accelerate healing
- Stretching tight muscles around your buttock hip and legs
- Soft tissue massage to relieve tight muscles and to reduce compression of the sciatic nerve.
- Advice on how to modify activity
- Exercises to strengthen the muscles to improve balance once pain and numbness has settled
Careful assessment by your physiotherapist will determine which factors have contributed to the development of the condition, and treatment will be tailored around this to ensure you make the best possible recovery.
Contact Us
Referred pain
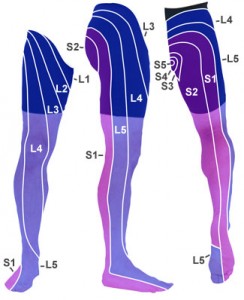 What is referred pain?
What is referred pain?
Pain felt in the buttocks is commonly referred from the lower back. There does not necessarily have to be pain in the lower back as well for pain to be referred into the buttocks. Problems in the lower back such as disc prolapse, spondylolysis and spondylolysthesis may refer pain to the buttocks.
Physiotherapy for referred pain
The physiotherapists at Platinum Physiotherapy commonly assess and treat people with referred pain.
Your physiotherapist will conduct a thorough assessment to identify the problems in your lower spine and develop an individualised treatment program to get you back to a level you were previously, as soon as possible. Physiotherapy treatment for referred pain may involve:
- Joint mobilisation and manipulation of the lumbar spine causing the referred pain
- Heat therapy
- Soft tissue massage to release muscle tension
- Exercise programme that will stretch and strengthen the muscles supporting the lumbar spine and the muscles in your buttocks and hip.
- Postural advice
- Ergonomic assessment
Physiotherapy treatment will help to relieve your pain so you can get back to everyday activities with confidence and success.
Contact Us
Sacroiliac Joint Pain
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
The sacroiliac joints sit between the sacrum and the ilia, at the back of the pelvis, and there are several dysfunctions that can exist in this area causing pain.
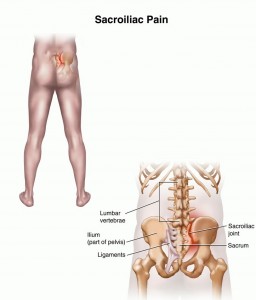 What is Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
What is Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction is an abnormality in the mechanics of the joint, which puts abnormal pressures on the joint surfaces, ligaments and surrounding muscles, causing pain. There are many different possible causes of the dysfunction due to the many different twisting forces applied to that area when moving the legs.
What causes Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
There are many causes of SI joint dysfunction which may include:
- Direct trauma such as a fall or a car crash.
- Mechanical imbalance, like a discrepancy in leg length.
- Repeated stress on the joint during various activities
- Inflammatory disorders such as Ankylosing Spondylitis
Hormones released during pregnancy allow ligaments holding the SI joints together to relax causing increased movement in the joints and can lead to increased stresses and abnormal wear.
What are the symptoms/effects of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction?
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction typically causes a dull aching pain at the base of the spine. The pain can vary from an ache to being sharp in nature with certain movements such as bending, lifting or rolling over in bed. Sometimes there is referred pain in the groin, buttock or the back of the thigh, but this referred pain will rarely go below the knee.
Diagnosis of Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
A thorough history and physical examination by a doctor or physiotherapist will confirm a diagnosis of Sacroiliac Joint dysfunction.
Physiotherapy Treatment for Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
A person with Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction will benefit from physiotherapy treatment.
Pain in the SI joint is often related to either too much movement or not enough movement in the joint. An initial assessment with one of our experienced physiotherapist will identify the underlying cause of your pain and a treatment plan will then be developed accordingly.
Your physiotherapist at Platinum Physiotherapy will use hands-on techniques and teach you various exercises to reduce the pain and get you back to your everyday activities as quickly and as safely as possible.
Physiotherapy will depend you current symptoms and lifestyle but may include:
- Advice about how to stay as active as possible while you are recovering
- Hot and cold therapy
- Joint mobilisation or manipulation
- Stretching and stabilising exercises to increase muscle strength and length in your spinal and abdominal muscles
- Soft tissue massage
- Advice on a sacroiliac belt to help stabilise the SI joints
Advice about orthotics if a discrepancy in leg length is the cause of the dysfunction
You will be supported throughout your rehabilitation program to ensure you make the best possible recovery.




![axa_ppp_logo[1]](https://www.platinumphysio.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/axa_ppp_logo1.gif)

![cigna[2]](https://www.platinumphysio.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/cigna2.png)