
Shoulder & Arm
Normal function of the shoulder and arm is vital for completing activities of daily living and popular sports. A reduction in shoulder and arm function can lead to a lowered quality of life.
Our specialised physiotherapists at Platinum Physiotherapy have extensive experience in designing specific rehabilitation programs for the shoulder complex and upper limb. Common shoulder problems that we treat at Platinum Physiotherapy include:
- AC Joint Pain
- Fractured Clavicle
- Frozen Shoulder
- Referred Pain
- Rotator Cuff
- Shoulder Dislocation
- Shoulder Impingement
- Shoulder Instability
- Bicep muscle tear
- Tricep muscle tear
- Rupture of the long head of biceps
- Biceps tendinopathy
- Fractured shaft of humerus
- Golfers Elbow
- Tennis Elbow
Our physiotherapists provide comprehensive assessment and treatment of common shoulder and upper limb pathologies. An initial assessment with one of our specialised physiotherapists will look at your current symptoms, movement and muscle strength.
A combination of treatments will be used to resolve these frustrating and often debilitating injuries. These include massage, stretching of muscles, mobilisation and manipulation to the neck and upper spine, strapping and a detailed functional rehabilitation program that addresses strengthening, the correction of predisposing factors and a graduated return to activity
Contact Us
AC Joint Pain
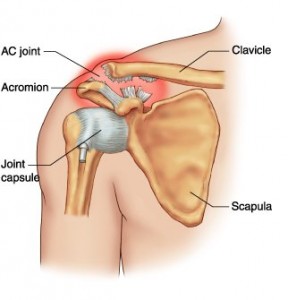 What is AC joint dislocation?
What is AC joint dislocation?
Acromio-clavicular (AC) joint dislocation is when the joint between the clavicle (collar bone) and acromian (shoulder blade) becomes displaced or shifted due to damage to the ligaments that join the two bones.
What causes AC joint dislocation?
This injury can be caused by falling on your shoulder, elbow or outstretched arm.
Types of AC joint dislocation?
AC joint dislocation is classified into different grades, depending on the amount of ligament damage. The types of AC joint dislocation include:
Type I – This is only a mild sprain of the acromioclavicular ligament with an intact coracoclavicular ligament.
Type II – This inloves a tear in the acromioclavicular ligament and may involve damage to the coracoclavicular ligaments.
Type III – The acromioclavicular joint capsule and coracoclavicular ligaments are both torn.
Type IV – This is a type III injury with avulsion (breaking) of the coracoclavicular ligament from the clavicle, causing the clavicle to move posteriorly.
Type V – This is type III but with more movement of the clavicle.
What are the symptoms/effects of AC joint dislocation?
Symptoms include pain at the end of the collar bone or when you move your shoulder joint, especially with the arms above your shoulders. Dependent on how severe the injury is, you may experience some swelling and also feel a little bony lump where the collar bone sticks up.
Physiotherapy treatment for AC joint dislocation?
Treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy, will initially help to relieve your pain and swelling and improve your function and return to sports in the long term.
Your rehabilitation program will be tailored to you and depend on the severity or grade of the dislocation.
Our Physiotherapists provide comprehensive assessment and treatment for people with AC joint dislocation. People with undisplaced injuries will require physiotherapy for approximately 6 weeks. Major dislocations may require surgical stabilisation, in which case physiotherapy will be involved in promoting your recovery following your operation. A sling may be used initially after the injury to promote healing. Physiotherapy treatment is vital after your shoulder has been immobilised for a few weeks to get the arm moving effectively and return you to your sporting or everyday activities as soon as possible.
The treatment may include:
- Cold therapy to reduce swelling
- Taping to facilitate normal alignment of the shoulder
- Gradual range of movement exercises to prevent stiffness and restore joint flexibility
- Once pain free range of movement has been achieved a structured strengthening exercise program will be developed to strengthen muscles around the shoulder joint
- Joint mobilisation
- Soft tissue massage
- Sport specific exercises to start to introduce you back to the activities you enjoy safely and effectively
Our specialised physiotherapists will restore your range of movement, muscle strength and function in order to return you safely and as quickly as possible back to sport or everyday tasks.
Contact Us
Fractured Clavicle
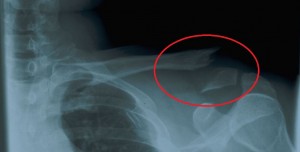 What is a fractured clavicle?
What is a fractured clavicle?
A fractured clavicle or collar bone is a breaking or splintering of the collar bone (the bone that runs along the front of the shoulder to the breast bone, located just below your neck). It is the most commonly fractured bone in the body.
What causes a fractured clavicle?
You can fracture your collar bone if you fall badly onto an outstretched arm or fall on the shoulder. A collision when doing contact sports such as rugby can also cause a fracture. Collar bone fractures are usually as a result of a physical injury and the bone most often fractures in its middle third.
What are the symptoms of a fractured clavicle?
There are various symptoms of a fractured collar bone, but if a fracture occurs you will usually know about it as it’s very painful.
Apart from the pain, other symptoms include swelling and bruising around the broken bone, a bony deformity may be seen or felt and once the swelling has gone down it is often easy to feel the fracture through the skin
Diagnosis of a fractured clavicle
If you suspect you may have broken your collar bone you should see your GP or local A&E immediately who will confirm a diagnosis. You may then be provided with a sling to rest the affected area. There are various types of slings available, most common been what is referred to as a ‘figure of eight’ splint.
Physiotherapy for a fractured clavicle
A person with a fractured clavicle will benefit from physiotherapy.
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy will help rebuild your muscle strength and flexibility in a safe and effective way.
Our physiotherapists will ensure you make a full recovery and return back to normal activities as quickly as possible by providing treatment individualised to you which may include:
- Ice therapy to reduce swelling and pain
- Ultrasound to accelerate healing
- Active and passive range of movement exercises to gradually restore pain free range of movement
- Strength training exercises to increase the strength of the tendons and muscles
- Exercises tailored to your sporting activity to maximise achievement with this as soon as possible
- A fractured collar bone will take between four to eight weeks to heal.
Your physiotherapist will ensure that pain and swelling is reduced before commencing a structured rehabilitation program tailored to your needs and physical activity, to ensure you make a full recovery as soon as possible.
Contact Us
Frozen Shoulder
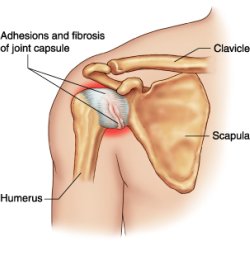 What is a Frozen Shoulder?
What is a Frozen Shoulder?
A frozen shoulder or adhesive capsulitus is inflammation of the connective tissue surrounding the shoulder joint which causes pain and stiffness and affects the ability to move the shoulder. Frozen shoulder reduces normal movement in the shoulder joint and, in some cases, it can prevent movement in the shoulder altogether. Frozen shoulders affect around 3% of the population and are slightly more common in women and those who suffer from diabetes.
What causes a frozen shoulder?
Frozen shoulder often occurs with no explanation. Some people may develop a frozen shoulder after a traumatic injury, but this is not always the case. There are some factors that make suffering from a frozen shoulder more common. These include:
- Shoulder trauma or surgery – if you have a shoulder injury frozen shoulder may occur, but not always. Surgery also increases the risk, especially if it is followed by a sustained period of joint immobilisation
- Age and gender – You are most likely to suffer from a frozen shoulder between the ages of 40 and 60, and as previously mentioned, women are more prone to suffering from a frozen shoulder than men
- Endocrine disorders – people who have diabetes or thyroid problems are particularly at risk from suffering from a frozen shoulder
- Other systemic conditions – heart disease and Parkinson’s diseases have been associated with an increased risk of developing a frozen shoulder.
What are the symptoms of a frozen shoulder?
Pain and stiffness in the shoulder joint, pain at night when lying on the affected side and limited range of motion.
A frozen shoulder tends to have three ‘stages’ to it:
- You will suffer some pain but will notice that you have limited movement (Freezing stage)
- The pain will ease off, but movement will become very limited (Frozen Stage)
- Finally the shoulder loosens up and returns to normal with full movement. (Thawing Stage)
It can take between two – three years for all these phases to occur. In younger people who are active, the whole process can sometimes be reduced to as little as 10 – 12 weeks.
Diagnosis of a frozen shoulder
A frozen shoulder can be diagnosed on examination by a physiotherapist. An X-Ray is occasionally taken to confirm that there are no other problems or possible causes for the shoulder pain.
Physiotherapy Treatment for a frozen shoulder
At Platinum Physiotherapy, our specialised physiotherapists are experienced at assessing and treating people with a frozen shoulder. Physiotherapy treatment will promote recovery and ensure you get your shoulder moving normally so you can continue with everyday activities with independence.
Structured exercise program including and specific stretching and strengthening exercises, to increase the range of movement in the shoulder joint and to minimise the loss of muscle. Exercise and stretching the affected shoulder is integral to ensure your shoulder returns to its normal functionality
Ultrasound
Advice about cortisone injections (used to decrease the inflammation in the frozen shoulder joint and help reduce pain. They also help allow more agility when stretching and exercising. Cortisone is only effective when used in conjunction with physiotherapy).
Physiotherapy treatment will keep your shoulder joint mobile with regular exercise tailored to you and improve pain, stiffness and functional ability.
Contact Us
Referred Pain
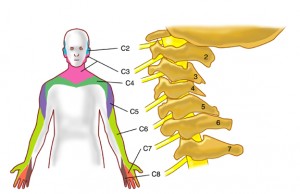 What is referred pain?
What is referred pain?
Pain is commonly referred to the shoulder and upper arm from other areas of the body. Dysfunction within the neck frequently causes referred pain to the shoulder region.
Physiotherapy for referred pain
Our physiotherapists at Platinum Physiotherapy commonly assess and treat people with referred pain.
Your physiotherapist will conduct a thorough assessment to understand the nature of your referred pain and develop an individualised treatment program to get you back to a level you were previously, as soon as possible.
Physiotherapy treatment for referred pain may involve:
- Joint mobilisation and manipulation of the affected joints causing the referred pain
- Soft tissue massage to relieve tight muscles groups
- Stretching exercises to relieve pain and stiffness
- Strengthening exercises to increase joint stability and to maximise potential with everyday activities
- Postural advice
- Ergonomic assessment
- Physiotherapy treatment will help to relieve your pain so you can get back to everyday activities with confidence and success.
Rotator Cuff
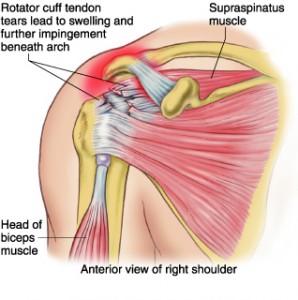 What is the rotator cuff?
What is the rotator cuff?
The rotator cuff is a group of tendons and muscles that hold the ball of the shoulder joint in place and provides mobility and strength.
A great deal of pressure and strain is put on these muscles if you play racket sports or partake in throwing events where your arm is above your head a lot.
The rotator cuff muscles are an overlapping series of tendons and these can become torn leading to pain and restricted movement of the arm. A torn rotator cuff can happen following a trauma to the shoulder or just through ‘wear and tear’.
Diagnosis of a rotator cuff injury?
A diagnosis of a rotator cuff injury can be made by a physiotherapist following a thorough physical examination.
What causes a rotator cuff injury
A rotator cuff injury can be caused by repetitive throwing and strain of the muscles or general degeneration which normally affects older people, smokers, or those having had cortisone injections Many athletes, like pitchers in baseball and javelin throwers, suffer of such injuries due to the repetitive movement of their shoulders.
What are the symptoms of a rotator cuff injury?
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff include difficulty in lifting the arm and pain on the outside of the shoulder possibly travelling down into the arm. Pain in the shoulder can get worse at night and there is often stiffness in the shoulder joint
Physiotherapy treatment for a rotator cuff injury
At Platinum Physiotherapy we have specialised physiotherapists who will provide individualised assessment and treatment for your rotator cuff injury.
Physiotherapy treatment will ensure you regain your range of movement, muscle strength and function, it may include:
- Muscle imbalance exercises
- Ultrasound
- Trigger point treatment
- Soft-tissue massage
- Strengthening and stretching exercises of the relevant muscle groups
Things you can do yourself
- Rest
- Cold therapy: Put a cold pack (typically an ice pack applied for 20 minutes) directly on the injury
- Thermotherapy: Apply heat (typically in the form of heated pads, warms packs or lamps) to the areas of the body causing pain. NB. Often Cold therapy and
- Thermotherapy are alternated, with the cold application happening first and last
- Use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as ibuprofen (Always seek the advice of a medical professional).
Shoulder Dislocation
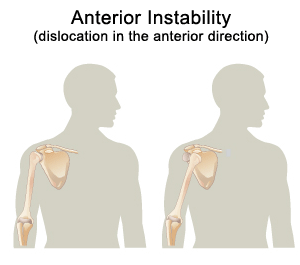 What is a shoulder dislocation?
What is a shoulder dislocation?
A shoulder dislocation is when the ball of the shoulder joint pops out of the shoulder socket. It is one of the most common sporting injuries sustained in contact sports such as rugby. The dislocation can either be an anterior or posterior dislocation where the arm appears out of position either pointing forwards or backwards.
What causes shoulder dislocation?
Contact sports and hitting your shoulder hard against a solid object can dislocate the shoulder. An anterior dislocation is the most common shoulder dislocation, when the top of the humerus (arm bone) shifts and sits in front of the shoulder blade.
Diagnosis of a shoulder dislocation?
If you suspect you have dislocated your shoulder you should seek medical treatment immediately to prevent further damage to the shoulder. Your GP or A&E doctor may treat your dislocated shoulders by manipulating the shoulder back into place. This is usually followed up with an x-ray to ensure the shoulder has been put back into place properly, and no other bones were fractured around the shoulder as a result of the manipulation. Your arm will then be placed in a sling for several weeks to help your shoulder recover.
What are the symptoms of a shoulder dislocation?
Symptoms of a shoulder dislocation may include:
- Sudden onset of acute shoulder pain
- A loss of sensation or feeling on the outside of the shoulder (this symptom could indicate possible damage to the nerve supplying the shoulder and arm)
- Swelling
- Muscle weakness
- Bruising
Physiotherapy for a shoulder dislocation?
Physiotherapy at Platinum Physiotherapy following your shoulder dislocation will gradually restore the range of motion to the shoulder and strengthen the muscles around it, to prevent re-injury and return you to your everyday activities and sports.
Your physiotherapist will initially assess your range of movement, muscle strength and function after your sling has been removed, in order to develop a progressive treatment program to help you get back to the level you were previously.
Physiotherapy treatment may include:
- Active and passive movement to keep the range of movements in the shoulder as well as the elbow, wrist and hand.
- Exercise to strengthen the muscles around your shoulder to increase joint stability and prevent re-injury.
- Advice about how to use your arm safely with everyday activities
- Functional and sport specific exercises. Your physiotherapist will give you exercises that are as similar as possible to the movements you do during your everyday activities.
Your physiotherapist will help you return to the activities you enjoy as soon as possible, by regaining pain free range of movement and strengthening your shoulder muscles in an exercise program suited to you and your hobbies.
Contact Us
Shoulder Impingement
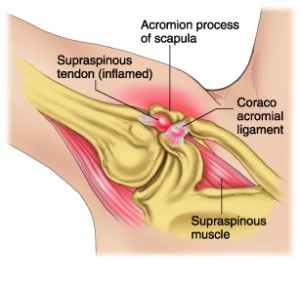 What is a shoulder impingement?
What is a shoulder impingement?
Shoulder Impingement is the most common shoulder problem and happens when the rotator cuff tendons get trapped in the shoulder joint causing pain, weakness and loss of function.
What causes shoulder impingement?
Shoulder impingement may be caused by a variety of factors such as:
- Overuse causing irritation of the structures in the shoulder joint. This is a common injury in swimmers, throwers, racket players and sports people who make repetitive movements with their arms above their shoulders.
- A trauma such as an accident or a fall
- Shoulder instability including rotator cuff weakness or capsule laxity
- Bony anatomical factors such as bone spurs caused by wear and tear of the joint between the collarbone and the scapula, called the acromioclavicular (AC) joint.
- Poor posture
Diagnosis of shoulder impingement
A diagnosis of shoulder impingement can be made by a physiotherpaist or doctor. Your physiotherpaist or doctor will ask you detailed questions about your activities and conduct a thorough assesment to confirm a diagnosis.
What are the effects/symptoms of shoulder impingement?
Symptoms of shoulder impingement include:
- Pain in the shoulder when the arm is lifted above the shoulder, forwards and upwards.
- Swelling in the shoulder area
- Difficulty rolling onto the affected shoulder or sleeping on it
Physiotherapy for shoulder impingement
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy will improve the strength in the muscles of the rotator cuff to help control the stability of the shoulder joint and decrease impingement of the rotator cuff tendons.
Your physiotherapist will create an individualised exercise program of restore range, strength, stability for your shoulder and rotator cuff which may include:
Stretching exercises to relieve pain and stiffness
Progressive muscle strengthening program which may include closed chained exercises, strengthening exercises through range and core stability exercises. Some of the exercises will be designed to get your shoulder working in ways that are similar to your work tasks and sport activities
- Postural advice
- Advice about how to avoid future problems and return to activity safely and effectively
- Your physiotherapist will guide you through a program suited to you so that you make a full recovery
Shoulder Instability
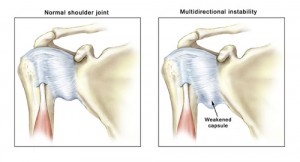 What is shoulder instability?
What is shoulder instability?
Shoulder instability occurs when the structures that surround the shoulder joint do not work to hold the shoulder in the socket. If the joint is too loose, is may slide partially out of place, a condition called shoulder subluxation. If the joint comes completely out of place, this is called a shoulder dislocation. People with shoulder instability often complain of an uncomfortable sensation that their shoulder may be about to slide out of place.
What causes shoulder instability?
Causes of shoulder instability may include injury such as a shoulder dislocation. Following trauma the shoulder joint often remains unstable as the ligaments and cartilage that maintain the shoulder in the socket have become stretched or torn. In other cases, athletes such as volleyball players and swimmers, who do repeated shoulder movements may gradually stretch out the joint capsule making the shoulder muscles weak and causing the ball of the humerus to slip around too much within the shoulder. Eventually this can cause irritation and pain in the shoulder.
Types of shoulder instability
Shoulder instability may be forwards (anterior), backwards (posterior), downwards (inferior) or multidirectional.
- Anterior instability – may be caused by either trauma, causing a dislocation, or atraumatic with a gradual onset. This type of instability is treated with an intensive rehabilitation program focusing on the strengthening of the rotator cuff muscles and scapular stabilising muscles.
- Posterior instability – is most commonly seen in athletes. It is treated with strengthening and control exercises for the posterior stabilising muscles.
- Multidirectional instability – is a combination of instabilities and is usually atraumatic. Multidirectional instability is often associated with joint hypermobility syndrome but can also be caused by repetitive trauma. Treatment involves strengthening of the shoulder stabilising muscles.
Diagnosis of shoulder instability
A physiotherapist or your GP can diagnose shoulder instability primarily through your medical history and a physical examination. Your doctor may order an X-ray to help confirm that your shoulder was dislocated or injured in the past.
What are the symptoms/effects of shoulder instability?
Symptoms of shoulder instability include:
- Subluxation – when the shoulder slips in certain positions, and the shoulder may actually feel loose. This commonly happens when the hand is raised above the head, for example while throwing.
- Pain – if your shoulder subluxes the people usually experience a quick feeling of pain, like something is slipping or pinching in the shoulder
- Frequent dislocations – this is usually very obvious and painful and the shoulder looks abnormal.
Physiotherapy for shoulder instability
At Platinum Physiotherapy, we provide specialised physiotherapy treatment for people with shoulder instability. Physiotherapy for shoulder instability will strengthen the muscles around the shoulder joint and help maintain the shoulder in a proper position.
Our physiotherapists integrate a global approach to rehabilitation incorporating the person’s whole body.
Your rehabilitation program will be developed following an initial assessment and tailored to you, to ensure you get the most out of your treatment.
Our rehabilitation focuses on the strengthening of scapula stabilising muscles and shoulder stability muscles. This is achieved with closed chain rehabilitation, rotator cuff strengthening, plyometrics and proprioceptive exercises.
Your rehabilitation program will also be functional and specific to your individual lifestyle. Physiotherapy treatment modalities used may include swiss ball exercises, medicine ball work, electrotherapy and rubber resistance band exercises.
Contact Us
Bicep muscle tear
What is a bicep muscle tear?
A bicep muscle tear is a condition characterised by tearing of one or more tendons or muscle bellies of the bicep muscle and caused by stress and pressure on your biceps, which results in pain and weakness.
What causes a bicep muscle tear?
A biceps muscle tear is caused by sudden or excessive contraction of the biceps muscle. This commonly affects weightlifters and other athletes that forcefully use the arm, such as lifting weights overhead, forceful arm elevation activities or bending of the elbow against resistance (such as performing chin ups or biceps curls).
A biceps muscle tear may also be caused by gradual trauma associated with repetitive or prolonged activities placing strain on the biceps tendon.
Diagnosis of a biceps tear
If you suspect you have torn your bicep a thorough examination from your GP or a physiotherapist will confirm a diagnosis. Further investigations such as an X-ray or MRI may also be required to rule out other injuries.
What are the symptoms/effects of a bicep muscle tear?
Symptoms of a bicep muscle tear include:
- Sudden onset of pain in the front of the shoulder, upper arm or elbow
- Swelling – the torn bicep looking bigger than the bicep on the opposite arm
- Weakness – it may be difficult to bend your elbow or turn your palm upwards
- Stiffness
- Bruising
Physiotherapy for a bicep tear
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy is vital to promote the healing process, ensure an optimal outcome and reduce the likelihood of future injury.
Physiotherapy treatment will be focused on reducing pain, improving muscle strength and flexibility and returning you back to your sporting and everyday activities as soon as possible. Physiotherapy treatment may include:
- Ice and heat therapy to relieve pain
- Ultrasound to accelerate healing
- Soft tissue massage to reduce discomfort and stiffness
- Stretches to improve range of movement
- Progressive muscle strengthening exercises
- Joint mobilisation
- Advice on how to modify your activity during your recovery
Your rehabilitation program will be suited to you which will emphasise a graded return to activity to ensure you make the best possible recovery.
Contact Us
Tricep muscle tear
What is a tricep muscle tear?
A tricep muscle tear is inflammation of the tricep muscle caused by tearing of the muscle belly or tendons. A tricep muscle tear is likely to occur when the tricep muscle is placed under pressure but can also be caused by repetitive movements, such as throwing. Tricep muscle tears are common is athletes that lift heavy weights without warming up correctly.
What causes a tricep muscle tear?
A tricep muscle tear is caused by stress placed on the tricep muscle and commonly affects weightlifters and other athletes that forcefully use the arm, such as lifting too much weight or straightening the elbow against resistance.
A tricep muscle tear may also be caused by repetitive strain on the muscle from prolonged activities which place gradual pressure on the tricep muscle, like throwing, hammering or playing tennis.
Diagnosis of a tricep tear
A doctor or a physiotherapist will confirm a diagnosis of a tricep tear following a subjective and objective examination. Further investigations such as an X-ray or MRI may also be required to rule out other injuries.
What are the symptoms/effects of a tricep muscle tear?
Symptoms of a bicep muscle tear include:
- Sudden onset of pain
- Swelling
- Weakness – it may be difficult to straighten your elbow
- Bruising
Physiotherapy for a tricep tear
Physiotherapy treatment is strongly recommended following a tricep injury to rebuild the strength and flexibility in the tricep muscle safely and effectively during your recovery.
At Platinum Physiotherapy our specialised musculoskeletal physiotherapists are experienced at treating tricep muscle tears and will hasten your healing and recovery and prevent re-injury. Physiotherapy treatment may include:
- Ice and heat therapy to relieve pain
- Ultrasound to promote healing
- Soft tissue massage to reduce pain and stiffness
- Progressive exercise program including stretches and strengthening exercises
- Joint mobilisation
- Advice on how to modify your activity during your recovery
Your physiotherapist will advise and support you throughout your rehabilitation for the best possible outcome both in the short and long term.
Contact Us
Rupture of the long head of biceps
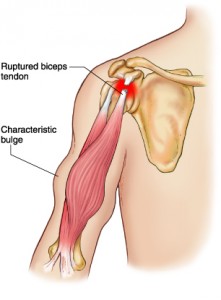 What is a rupture of the long head of the biceps?
What is a rupture of the long head of the biceps?
A rupture of the long head of the biceps is a complete tear of the main tendon that attaches the top of the biceps muscle to the shoulder. It commonly affects athletes during weightlifting but can also affect people who fall with the arm outstretched resulting in pain and loss of function. When people tear their biceps tendon, they can also damage other parts of the shoulder, such as the rotator cuff tendons
What causes a rupture of the long head of the biceps?
A rupture of the long head of the biceps may be caused by:
Wear and tear of the tendon making the tendon weaker and therefore more susceptible to tears
Overuse or repetitive movement of the shoulder can cause inflammation of the tendon (tendonitis). Repetitive overhead sports, such as swimming or tennis can lead may increase the chances of the fraying and eventually rupture of the bicep tendon.
Injury such as a fall on an outstretched hand or lift something too heavy, you can rupture your biceps tendon.
What are the effects/symptoms of a rupture of the long head of the biceps?
Immediate symptoms may include hearing and feeling a pop or snap in the top of the shoulder followed by sharp pain.
Soon afterward, bruising may develop in the middle of the upper arm and spread down to the elbow. The arm may also feel weak at when trying to bend the elbow or lift the shoulder.
Diagnosis of a rupture of the long head of the biceps
A thorough physical examination by your doctor or by a physiotherapist will confirm a diagnosis of a long head of bicep rupture. You may also have an X-Ray or MRI to see if there are any other problems with your shoulder.
Physiotherapy treatment for a rupture of the long head of the biceps
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy will relieve the pain and swelling and increase muscle strength and range of movement to help you return to activity sooner.
Your physiotherapist will initially assess your arm in order to develop an individualised treatment program which may include:
- Ice and ultrasound to ease pain and promote healing
- Advice on how to rest your shoulder while it is healing and how to gradually return to activity without putting extra strain on the sore area.
- Exercises are used to gradually strengthen other muscles that help do the work of a normal biceps muscle.
- Stretching and soft tissue massage to relieve any tension
As you progress, your physiotherapist will teach you exercises to strengthen and stabilise the muscles and joints of the elbow and shoulder. Your exercises will work your arm in ways that are similar to your work tasks and sport activities so that you can return to these with confidence and success.
Biceps tendinopathy
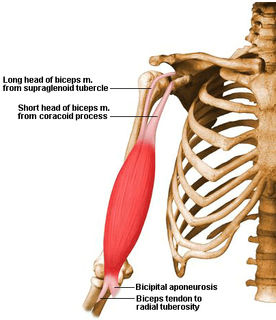 What is biceps tendinopathy?
What is biceps tendinopathy?
Biceps tendinopathy is a term which describes pain and tenderness in the shoulder region due to degeneration and/or inflammation to the biceps tendon. This may occur traumatically due to a high force going through the biceps tendon such as lifting heavy weights or falling on an outstretched hand or due to gradual wear and tear associated with overuse.
What causes biceps tendinopathy?
Biceps tendinopathy can be caused by many factors including:
- Poor lifting techniques
- Long term repetitive activities placing strain on the biceps tendon
- Shoulder Impingement
- Poor posture
- Direct trauma such as a fall
- Wear and tear of the tendon (degenerative changes)
What are the effects/symptoms of biceps tendinopathy
People with biceps tendinopathy experience pain in the front of the elbow which may increase with activity during activity such as carrying heavy shopping, performing biceps curls or chin ups.
Occasionally people may notice swelling at the front of the elbow and experience weakness when attempting to lift objects.
Diagnosis of biceps tendinopathy
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist or doctor will diagnose biceps tendinopathy. Occasionally, further investigations such as an ultrasound, X-ray or MRI scan may be required to assist with diagnosis and assess the severity.
Physiotherapy for biceps tendionpathy
Early physiotherapy treatment is vital to promote recovery and for long term success.
At Platinum Physiotherapy, our specialised musculoskeletal physiotherapists will develop an individualised and graduated rehabilitation program to ensure an optimal outcome. Your physiotherapist will also advise you on the exercises most appropriate for you and when they should be commenced.
Physiotherapy treatment may comprise of:
- Ice or heat treatment to reduce swelling and pain
- Soft tissue massage to relieve pain and stiffness
- Ultrasound to accelerate healing
- Stretching exercises
- Joint mobilisation
- Exercises to improve strength and flexibility
- Advice and support on how to modify your activity
Your physiotherapist will guide you through the best course of treatment in order to relieve your pain and improve your success with every day and sporting activities.
Contact Us
Fractured shaft of humerus
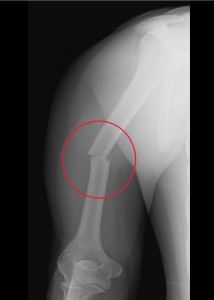 What is a fractured shaft of humerus?
What is a fractured shaft of humerus?
A fractured shaft of humerus is when the middle part of the bone in the upper arm (humerus) breaks. The humerus connects the shoulder to the elbow joint. A fracture of the humeral shaft involves damage to the humerus but may also affect the elbow and shoulder joints, and the soft tissue around the fracture site, including nerves, tendons, ligaments, and blood vessels.
What is the cause of a fractured shaft of humerus?
Fractures to the humeral shaft are most commonly caused by direct stress such as a blow to the arm or a fall onto an outstretched arm. The risk of a fracture of the humeral shaft also increases with:
Contact sports such as football or hockey
A history of bone or joint disease, especially osteoporosis
Obesity
What are the symptoms/effects of a fractured shaft of humerus?
Symptoms of a fractured shaft of humerus may include:
- Pain especially when moving the shoulder or elbow
- Limited movement
- Swelling
- Abnormal sensation over the back of the hand, and weakness of some of the muscles of the hand and wrist if the radial nerve is damaged.
Diagnosis
If you suspect you have fractured your arm you need to seek medical advice as soon as possible. You will usually have an X-ray to see the extent of your injury and to confirm a diagnosis of a fracture.
Most people are then provided with a sling or brace, and with time the fracture will heal.
Physiotherapy treatment for a fractured shaft of humerus
Physiotherapy treatment is strongly advised following immobilisation in a sling or brace to help regain muscle strength and range of movement and get you back to the activities you enjoy.
At Platinum Physiotherapy, physiotherapy will promote fracture realignment and healing and maximise function.
Physiotherapy treatment may involve:
- Actively exercising all muscle groups that in the upper arm and the wrist to build strength and flexibility
- Advice on when to resume normal activities gradually
- Soft tissue massage and heat therapy to relieve any stiffness or pain
- Sport specific exercises
The average healing time for this type of fracture is 6 to 8 weeks. Your physiotherapist will guide and support you through your rehabilitation program to ensure you get the most out of your treatment and gone to make a full recovery with every success in the long term.
Contact Us
Golfers Elbow
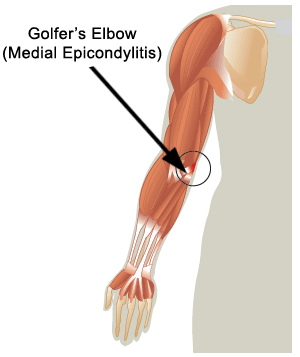 What is Golfers elbow?
What is Golfers elbow?
Golfers elbow or medial epicondylitus is a very similar condition to tennis elbow which is characterised by pain that affects the inside of elbow. Golfers elbow is of an overuse nature, associated with work-related or sporting activities.
What causes Golfer’s Elbow?
There are many activities that can cause Golfer’s Elbow such as working out at the gym or simply working in front of a computer for prolonged periods. These activities use the same muscles (wrist flexors and forearm pronators) repetitively and can result in the inflammation of common flexor tendon of the wrist where it attaches at the inside of the elbow. The causes of Golfer’s Elbow are similar to tennis elbow but pain and tenderness are felt on the inside of the elbow, on or around the joint’s bony prominence.
What are the symptoms of Golfer’s Elbow?
Symptoms include tenderness and pain at the inside of your elbow, made worse by bending the wrist, grasping and turning the palm downwards (pronation). The pain may also spread down the forearm. .
Physiotherapy for Golfer’s Elbow?
Physiotherapy treatment Platinum Physiotherapy will reduce your pain and facilitate your recovery by developing an individualised program suited to you. Your physiotherapy program may include:
- Neural and flexor muscle stretches, and progressive conditioning exercises to strengthen the area and prevent re-injury.
- Massage to relieve stress and tension in the muscles
- Myofascial release of the muscles around the elbow
- Electrotherapy
- Advice about supportive clasps or splints to off load the tendons during recovery
- Advice about steroid injections for persistent pain
Your physiotherapist will advice and support you throughout your treatment to ensure you make the best possible recovery and go on to make long term improvements to prevent re-injury.
Contact Us
Tennis Elbow
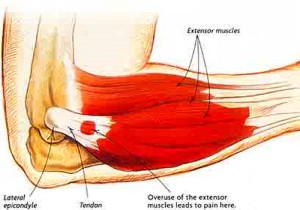 What is Tennis Elbow?
What is Tennis Elbow?
Tennis elbow is the inflammation and degeneration of the common extensor tendon of the forearm that attaches to the outside part (lateral epicondyle) of the humerus bone at the elbow. Tennis elbow is common amongst sports people and manual workers. Tennis elbow is not a diagnostic term, it is no more specific than back pain as a diagnosis. In fact this condition is more common in non tennis players than tennis players.
What causes Tennis Elbow?
Tennis elbow is the most common elbow injury, characterised by inflammation of the extensor tendon of the forearm muscles, which is caused by prolonged gripping such as driving, racket sports or even using a hammer.
The inflammation and pain associated with tennis elbow is due to tiny tears in a part of the tendon and in the muscle covering. After the initial injury heals, these areas are susceptible to tear again. Inflammation may also cut off the blood flow and pinch the radial nerve, one of the major nerves controlling muscles in the arm and hand.
Tennis elbow is most commonly a result of an overuse syndrome related to excessive use of the wrist in everyday or sporting activities.
What are the symptoms/effects of Tennis Elbow?
The symptoms of tennis elbow include pain on the outside of the upper forearm just below the bend of the elbow, which is made worse by wrist and gripping activities. This pain occasionally radiates down the arm toward the wrist.
Physiotherapy treatment for Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow is the most common elbow condition our physiotherapists at Platinum Physiotherapy treat. Physiotherapy treatment may involve:
- Massage to relieve stress and tension in the muscles
- Individualised exercise programme including, neural and extensor muscle stretches and progressive conditioning exercises to strengthen the area and prevent re-injury.
- Taping a band around your forearm to take pressure off the extensor tendons.
- Myofascial release of the forearm muscles
- Cross frictions to the tendon
- Electrotherapy such as Ultrasound to accelerate healing
- Advice about steroid injections for persistent pain and inflammation
- Physiotherapy treatment will reduce pain and inflammation and promote healing so that you can get back to the activities you enjoy as soon as possible.
Your treatment program will be tailored to you and include goals centred around your hobbies and lifestyle for the best possible outcome.
Contact Us




![axa_ppp_logo[1]](https://www.platinumphysio.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/axa_ppp_logo1.gif)

![cigna[2]](https://www.platinumphysio.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/cigna2.png)