
Wrist and hand
Our physiotherapists at Platinum Physio assess and treat many people with wrist and hand pain from an acute injury (such as a fall on an outstretched hand), or pain that has developed gradually as a result of overuse.
The wrist and hand is an incredibly complex and versatile system of bones, joints and tendons that we use thousands of times a day to carry out many functional activities.
Type of injuries to the wrist and hand we treat at Platinum Physiotherapy may include:
- Repetitive strain injuries
- Carpal tunnel
- Colles fracture of the wrist
- Dequervain’s tenosynovitus
- Osteoarthritis of the wrist
- Broken finger
- Dislocated finger
- Dupuytren’s contracture
- Trigger finger
- Hyperextension injury
Physiotherapy treatment is individually tailored your needs and designed to restore function and reduce pain so that you can return to your everyday activities with independence and confidence as soon as possible.
Many people benefit from physiotherapy including those who have injured their wrist and hand directly or have had surgery or are simply suffering from pain and discomfort.
Repetitive Strain Injury
What is a Repetitive Strain Injury?
Repetitive Stress Injury is an umbrella term used to describe a number of specific injuries caused by the repeated movement of a particular part of the body and commonly affects nerves, tendons and muscles. The incidence of this type of injury is becoming more widespread as many jobs now require people to make repetitive actions such as typing, or clicking a computer mouse. It can also occur frequently in sports, for example Achilles Tendinitis in basketball or Tennis Elbow in tennis.
What causes Repetitive Strain Injuries?
These injuries are often caused when stress is placed on a joint due to the same action being performed over and over. The two most common types of repetitive stress injuries are Tendonitis (inflammation of the tendon) and Bursitis (inflammation of a structure called the bursa which is a sac-like structure within a joint).
What are the symptoms/effects of a Repetitive Strain Injury?
The symptoms of a Repetitive Strain Injury may include:
- Pain which is aggravated by movement
- Swelling
- Redness
- Reduced range of movement
Physiotherapy treatment for Repetitive Strain Injuries
Platinum Physiotherapy will help you resolve your pain and get back to full function. Physiotherapy treatment may consist of exercises, stretches, and electrotherapy to accelerate healing, reduce pain and get you back to a full recovery.
Contact Us
Carpal tunnel
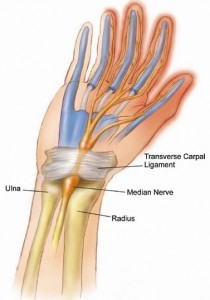 What is carpal tunnel?
What is carpal tunnel?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is compression of the median nerve which travels through the wrist causing pain and numbness of the thumb, index, long and radial half of the ring finger.
What causes carpal tunnel?
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is considered to be a form of repetitive stress injury, caused by repetitive movement (most commonly, from computer keyboard use). Other contributing factors include trauma or injury to the wrist that cause swelling, such as sprain or fracture, rheumatoid arthritis, mechanical problems in the wrist joint and fluid retention during pregnancy or menopause.
What are the symptoms/effects of carpal tunnel?
The symptoms of carpal tunnel usually start gradually, with frequent burning, tingling, or numbness in the palm of the hand and the fingers, especially the thumb and the index and middle fingers. Some people report decreased grip strength making it difficult to form a fist, grasp small objects, or perform other manual tasks. The symptoms often first appear in one or both hands during the night, since many people sleep with bent wrists squeezing the median nerve.
Physiotherapy for carpal tunnel
Physiotherapy treatment is very important to hasten the healing process and decrease the likelihood of re-injury.
A thorough assessment at Platinum Physiotherapy will determine what has contributed to the development of carpal tunnel and a treatment plan will be developed to ensure a speedy recovery.
Physiotherapy treatment may include:
- Advice about sufficient rest from any aggravating activities and how to modify tasks
- Ice and heat therapy
- Soft tissue massage
- Electrotherapy
- Advice about splints
- Range of movement exercises
- Strengthening exercises
- Advice about gradual return to everyday and sporting activities
Physiotherapy treatment will reduce your pain and numbness and regain the functional use of you wrist and hand so that you can get back to your everyday and sporting activities as quickly as possible.
Contact Us
Colles fracture of the wrist
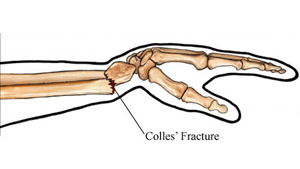 What is a Colles fracture?
What is a Colles fracture?
A Colles fracture is a fracture of the radius bone just above the wrist, which is commonly caused by a fall on an outstretched hand.
What causes a Colles fracture?
A Colles fracture occurs most frequently from a fall onto an outstretched hand, but any sudden force pushing the hand backwards (as might be experienced in a car accident) can be responsible for this type of fracture.
What are the symptoms/effects of a Colles fracture?
If you have fractured your wrist symptom may include:
- Pain
- ‘Dinner fork’ deformity due to the shape of the forearm
- Swelling
- Stiffness
Diagnosis of a Colles fracture
A diagnosis of a Colles fracture is usually made following a physical examination and an X-Ray. If you suspect you have broken your wrist you should seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Physiotherapy following a Colles fracture
A Colles fracture is usually supported in a plaster of Paris cast for about six weeks. Physiotherapy following removal of this cast is vital to regain movement and strength in your wrist and hand in a safe and effective way.
At Platinum Physiotherapy we are experienced at treating people following a Colles fracture and will get you back to you full function as quickly as possible.
Physiotherapy will reduce your pain, regain your range of movement, improve your muscle strength and return you to those activities you enjoy.
Treatments may include:
- Soft tissue massage to relieve tension and tight muscles
- Ice and heat therapy to relieve pain and stiffness
- Electrotherapy
- Passive stretching to regain range of movement
- Active range of movement exercises to gradually improve strength and function
- Strengthening exercises
- Advice about how to modify activities whilst your fracture is still healing
- Gradual return to hobbies and sporting activities
Your physiotherapist will develop a treatment plan suited to you and your lifestyle so that you make a full recovery.
Contact Us
Dequervain’s tenosynovitus
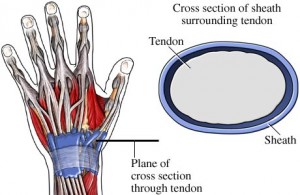 What is De quervain’s tenosynovitis?
What is De quervain’s tenosynovitis?
De quervain’s tenosynovitis is inflammation of the tendons on the thumb side of your wrist causing pain when turning the wrist, grasping or making a fist.
What causes De quervain’s tenosynovitis?
The exact cause of de quervain’s tenosynovitis is not known, however, any activity that relies on repetitive hand or wrist movement such as working in the garden, playing music, knitting, cooking, and lifting objects can aggravate the condition.
What are symptoms/effects of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis?
The symptoms of De Quervain’s tenosynovitis include pain and tenderness at the side of the wrist beneath the base of the thumb. There may also be swelling and redness in the area.
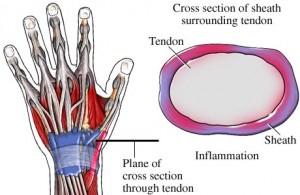 Diagnosis of De Quervains tenosynovitis
Diagnosis of De Quervains tenosynovitis
De Quervain’s tenosynovitis is diagnosed based on the typical appearance, location of pain, and tenderness of the affected wrist by either a physiotherapist or a doctor.
Physiotherapy for De Quervains tenosynovitis
Physiotherapy will identify the cause of irritation of the thumb tendons and provide an individualised program which will promote correct wrist and thumb positions, range of movement and strength of the wrist and hand and prevent future problems.
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy may include:
- Advice on how to modify activity during recovery
- Advice on forearm or thumb splints
- Ergonomic assessment of your workstation and the way you do work tasks
- Exercise program for the wrist and hand to regain pain free range of movement and help you regain independence with functional tasks.
- Ultrasound to promote healing
- Ice and heat therapy to relieve pain
As you progress, your physiotherapist will give you exercises to help strengthen and stabilise the muscles and joints in your hand and thumb. You will also be provided with exercises to improve fine motor control and dexterity. These exercises are designed to get your hand working in ways that are similar to your work tasks and sport activities.
Your physiotherapist will ensure that you can get back to your everyday activities pain free and to the best of your ability and teach you a number of ways to avoid future problems.
Contact Us
Osteoarthritis of the wrist and hand
What is osteoarthritis of the wrist and hand?
Osteoarthritis is the main form of arthritis and is known as the “wear and tear’’ of a joint. The wrist and hand are especially susceptible due to the tremendous amounts of pressure that is placed during everyday activities. Osteoarthritis causes damage to the cartilage, which results in stiffness and aching of the joints. Osteoarthritis can also follow a fracture or a bad sprain to the wrist. Osteoarthritis commonly develops at the base of the thumb, at the joint closest to the finger tip, and the middle joint of the finger.
What causes osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis can be caused by repetitive use of a particular joint in the body. In some people osteoarthritis is secondary to pre-existing damage to the joint for example, caused by fractures, ligament injuries, maldevelopment of the bone or joint or other types of arthritis.
What are the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the wrist and hand?
Symptoms of osteoarthritis may include:
- Stiffness and pain in the wrist or joints of the hand
- Reduced range of movement
- Your wrist may fill with fluid and feel tight, especially after using it
Physiotherapy for osteoarthritis of wrist and hand
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy will reduce pain, help to maintain wrist and hand function and increase the muscle strength to provide stability to the wrist joint, so that you can get back to your daily tasks with confidence and success.
Physiotherapy treatment may include:
- Heat therapy to alleviate pain
- Soft tissue massage to relieve stiffness and pain
- Advice about wrist braces and supports that may help to reduce your pain during activity as it removes stresses from the wrist.
- Range of movement and wrist strengthening exercises to protect the joint from shock and stress.
- Advice about how to modify activities and avoid certain movements such as lifting and carrying heavy loads to provide some relief and increase independence
Your physiotherapist will initially assess your pain, range of movement, strength and function in order to develop a rehabilitation program tailored to you and your lifestyle. Short and long term goals will then be developed so that you get the most out of your treatment and reach your maximum physical potential.
Contact Us
Broken finger
Fingers are easily injured and broken in everyday activities and sporting activities causing pain and swelling and can significantly interfere with writing, gripping, cooking, household activities or placing weight through the affected hand and fingers.
What causes a broken finger?
A broken finger commonly occurs in contact sports such as basketball or netball when the finger is bent forcefully in the wrong direction (such as a hyperextension force or a sideways force. A broken finger may also be caused by a collision with another person or falling onto the hand.
What are the symptoms/effects of a broken finger?
Symptoms of a broken finger include sharp pain and sometimes a deformed finger. As time goes on, swelling and bruising of the finger will occur and the finger will become stiff to move. Swelling is not as specific as pain and therefore may affect the adjacent fingers as well.
Diagnosis of a broken finger
If you suspect you have broken you finger you should seek medical attention. A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist or doctor will diagnose a dislocated finger. X-rays will also be taken to assist with diagnosis.
Treatment for a broken finger
Treatment for a broken finger usually involves immobilisation in a small splint for between 2 to 4 of weeks to allow the bone to heal.
If your finger is out of position, the deformity may need to be corrected, or “reduced.” This is usually done under local anesthesia. The finger is then put back in place to correct the deformity and a splint is applied for 4 weeks.
If the fracture has is unstable, or if the deformity cannot be corrected, then surgery may be necessary to realign and hold the broken fragments in place. Pins, plates, and screws can all be used to hold the fracture in the proper position.
Physiotherapy for a broken finger
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy should start as soon as possible with gentle range of movement exercises to keep you finger strong and flexible.
Following surgery or once the splint is removed, your physiotherapist will assess your range of movement, strength and function in order to develop an individualised treatment program which may include:
- Ice therapy and ultrasound to reduce swelling and pain
- Passive stretching to lengthen tight muscles
- Soft tissue massage to reduce stiffness
- Advice about how to modify everyday activities and prevent re-injury
- Progressive exercises program for your finger and hand to improve flexibility and strength and maximise function.
- Your individualised rehabilitation program will improve stability of the finger joint, prevent re-injury and get you back to everyday and sporting activities safely and effectively
Your physiotherapist will tailor activities to you and your hobbies and will ensure that your finger is returned to its original function and strength as soon as possible.
Contact Us
Dislocated finger
What is a dislocated finger?
A dislocated finger is a common injury characterised by tearing of the connective tissue surrounding one of the finger joints, due to excessive forces placed on the finger, which causes displacement of the bones, so they are no longer situated next to each other.
Damage to other structures such as tendons and bones may also occur as a result of a finger dislocation.
What causes of a dislocated finger
Dislocated fingers commonly occur in sporting activities such basketball, netball, cricket or football, when a specific incident bends the finger forcefully in the wrong direction (such as a hyperextension force or a sideways force). A direct blow to the point of the finger or a collision with another player may also cause a dislocation.
What are the symptoms/effects of a dislocated finger?
Symptoms of a dislocated finger include sudden onset of intense finger pain during the acute incident. This may be accompanied by a visible bump or deformity, swelling and bruising. These symptoms may be made worse by everyday activities such as opening jars or doors, writing, picking up objects and gripping.
Diagnosis of a dislocated finger
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist or a doctor will confirm a diagnosis of a dislocated finger. X-rays are also taken to rule out fractures and assist with diagnosis.
Physiotherapy for a dislocated finger
Treatment for a dislocated finger usually involves immobilisation in a splint for a number of weeks to allow the damaged connective tissue to heal and form a ‘scar’.
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy will commence with gentle exercises to maintain movement and strength and to prevent stiffness and pain. When the splint is removed your physiotherapist at will continue to advise you about activities and exercise to improve stability of the joint, prevent re-injury and get you back to everyday and sporting activities safely and effectively.
Physiotherapy for a dislocated finger will accelerate the healing process and ensure that you make the best possible recovery. Treatment may comprise of:
- Ice therapy and ultrasound initially to reduce swelling and pain
- Finger bracing or splinting
- Gentle range of movement exercises while the finger heals
- Advice about how to modify everyday activities and prevent re-injury
- Progression of exercises once the splint is removed to improve flexibility and strength in the wrist and hand
- Soft tissue massage to reduce stiffness
- Passive stretching to lengthen tight muscles
Your treatment program will be specific to you and your hobbies and will ensure that your finger is returned to its original function and strength as soon as possible.
Contact Us
Dupuytren’s contracture
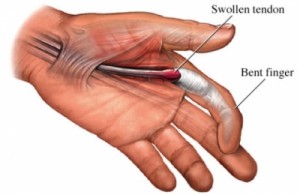 What is a Dupuytren’s contracture?
What is a Dupuytren’s contracture?
Dupuytren’s contracture is shortening of the soft tissue in the fingers causing the fingers to bend towards the palm and cannot be fully straightened.
What causes a Dupuytren’s contracture?
It is not clear what exactly causes Dupuytren’s contracture. However, the most common factor is genetics and up to 70% of people who develop Dupuytren’s contracture have a family history of the condition. The condition is also more common in men, people over the age of 40 and people of white northern European ethnicity.
What are the symptoms/effects of Dupuytren’s contracture?
The main symptoms of Dupuytren’s contracture are small nodules (thickening of connective tissue) on the palm of your hand making it difficult to straighten the finger. This may also be tender to touch.
As Dupuytren’s contracture progresses, your fingers may eventually be pulled into a permanently flexed (bent) position which makes it difficult to perform simple activities, such as cooking, swimming, playing a guitar or shaking someone’s hand.
Conventional treatment for Dupuytren’s contracture
In the early stages of the disorder, physiotherapy can slow or reverse the contracture.
At Platinum Physiotherapy, our physiotherapists understand that Dupuytren’s contracture affects everyone differently. An initial assessment with one of our physiotherapists will look at your range of movement, strength and current problems in carrying out daily activities.
Physiotherapy treatment may include heat, stretching, and soft tissue massage to control pain and to try to slow the progression of the contracture. Your physiotherapist may advise that you wear a splint that keeps the finger straight which is usually worn at night. You may also be provided with a home exercise program consisting of stretching and range of movement exercises to maximise function.
However, Dupuytren’s contracture is known to progress, so surgery may be needed at some point to release the contracture and to prevent disability in your hand.
Physiotherapy following surgery
Our physiotherapists also provide individualised treatment for people following surgery of a Dupuytren’s contracture.
Physiotherapy treatment following your surgery will regain your range of movement, relieve you pain and get you back to daily activities with independence and success as quickly and safely as possible.
Treatment following surgery may include:
- Soft tissue massage to relieve any stiffness and pain
- Passive stretching to improve flexibility and maximise function
- Active range of movement exercises
- Activities to improve dexterity, coordination and grip strength
- Gradual return to everyday activities that put stress on the fingers such as carrying heavy loads and cooking
Your rehabilitation program will be tailored to you so that you reach your optimal function and continue to make long term improvements.
Contact Us
Trigger finger
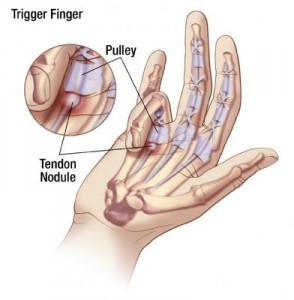 What is trigger finger?
What is trigger finger?
Trigger finger occurs when the tendon in the finger or thumb thickens and gets caught when the finger is bent towards the palm, resulting in a painful clicking or locking. Sometimes, the tendon will pop free and your finger will be able to move again, but it may become stuck in a permanently bent position.
What causes trigger finger?
There is often no apparent cause of trigger finger. However it is six times more common in women and more common in people who have previously injured their finger or thumb, for example, Dupuytren’s contracture and De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Other medical conditions such as diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and gout also increase the chance of developing trigger finger.
What are the symptoms/effects of trigger finger?
Symptoms of trigger finger may include:
- Pain at the base of the affected finger or thumb
- A nodule (a small growth or lump of tissue) at the base of the affected finger or thumb
- Stiffness or clicking when you move the affected finger or thumb, particularly first thing in the morning. Over time it may be difficult to straighten the finger or thumb and it may stay in a bent position
Treatment for trigger finger
Conservative treatment for trigger finger may include splinting and or steroid injections. Some people will be provided with a splint to wear at night time to prevent the finger becoming locked during the night. Approximately 80%of people can be successfully treated with a steroid injection into the finger or palm, to reduce swelling.
Physiotherapy treatment in conjunction with steroid injections and splinting will optimise your recovery.
Surgery may be required if conservative methods are not successful. Surgery is a simple, safe and quick procedure under local anaesthetic.
Physiotherapy for trigger finger
Our physiotherapists provide specialised hand therapy for people who do not require surgery and for people who have had surgery.
Physiotherapy treatment will help to reduce swelling, relieve pain and stiffness and regain functional movement of the finger, so that you can get back to your daily tasks as soon as possible.
Physiotherapy treatment may include:
- Ultrasound to reduce swelling and accelerate healing
- Soft tissue massage
- Joint mobilisation
- Passive stretching
- Supervised hand and finger exercise program to regain strength, dexterity and flexibility
- It is important to commence physiotherapy soon after diagnosis to prevent the condition from getting worse and to get you back to your normal level of functioning
Your physiotherapist will guide you through your individualised treatment program to ensure a speedy return to everyday tasks and activities, either at work or at home.
Contact Us
Hyperextension injury
What is a hyperextension injury?
A hyperextension injury is when the finger is straightened too far which can result is a ligament sprain causing pain, swelling and instability.
What cause a hyperextension injury?
A hyperextension injury is commonly caused by direct contact with another player or when tackling in sports such as basketball or netball when the finger is forced backwards.
What are the symptoms/effects of a hyperextension injury?
Symptoms of a hyperextension injury initially include a sudden onset of finger pain on the front, back or sides of the affected finger joint. There may also be an audible snap or pop sound at the time of injury. Swelling or bruising will often develop around the affected joint.
Diagnosis of a hyperextention injury
A thorough subjective and objective examination from a physiotherapist or doctor is sufficient to diagnose a hyperextension injury. An X-Ray may also be required to rule of any other injuries.
Your finger may then immobilised in protective taping or a protective brace for 2 to 4 weeks to stabilise the joint and allow healing to take place.
Physiotherapy for hyperextension injury
People with hyperextension injury will benefit from physiotherapy treatment.
Physiotherapy treatment at Platinum Physiotherapy will help you make the best possible recovery and get you back to your sporting and everyday activities by reducing pain and swelling and increasing range of movement and strength.
Physiotherapy treatment for a hyperextention injury may include:
- Protective taping or a protective brace to stabilise the joint and protect it from further damage.
- Advice about modifying activities to promote the healing process in the absence of further tissue damage.
- Ice and heat therapy to reduce pain and swelling
- Ultrasound
- Joint mobilisation
- Soft tissue massage
- Range of movement and strength exercises to maximise finger function. These exercises will be implemented as soon as pain allows and will be guided by your physiotherapist
Physiotherapy treatment will hasten the healing process and ensure you return to your sporting activities with confidence and success.




![axa_ppp_logo[1]](https://www.platinumphysio.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/axa_ppp_logo1.gif)

![cigna[2]](https://www.platinumphysio.co.uk/wp-content/uploads/cigna2.png)